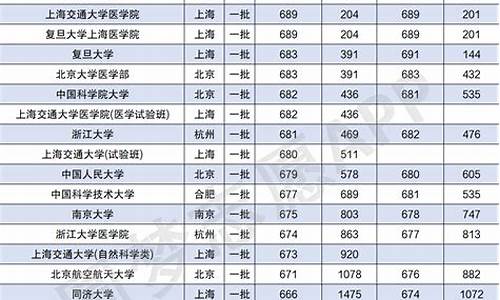
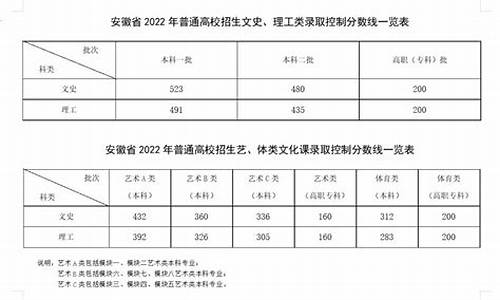
您现在的位置是: 首页 > 招生信息 招生信息
海南高考2020英语答案,高考海南英语答案
tamoadmin 2024-05-21 人已围观
简介1.2008海南省高考英语作文题目是什么?2009年普通高等学校招生全国统一考试(宁夏卷)数学(理工农医类)第I卷一, 选择题:(本大题共12题,每小题5分,在每小题给出的四个选项中 ,中有一项是符合题目要求的。(1) 已知集合 ,则 (A) (B) (C) (D) (2) 复数 (A
1.2008海南省高考英语作文题目是什么?

2009年普通高等学校招生全国统一考试(宁夏卷)
数学(理工农医类)
第I卷
一, 选择题:(本大题共12题,每小题5分,在每小题给出的四个选项中 ,中有一项是符合题目要求的。
(1) 已知集合 ,则
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
(2) 复数
(A)0 (B)2 (C)-2i (D)2
(3)对变量x, y 有观测数据理力争( , )(i=1,2,…,10),得散点图1;对变量u ,v 有观测数据( , )(i=1,2,…,10),得散点图2. 由这两个散点图可以判断。
(A)变量x 与y 正相关,u 与v 正相关 (B)变量x 与y 正相关,u 与v 负相关
(C)变量x 与y 负相关,u 与v 正相关 (D)变量x 与y 负相关,u 与v 负相关
(4)双曲线 - =1的焦点到渐近线的距离为
(A) (B)2 (C) (D)1
(5)有四个关于三角函数的命题:
: x R, + = : x、y R, sin(x-y)=sinx-siny
: x , =sinx : sinx=cosy x+y=
其中假命题的是
(A) , (B) , (3) , (4) ,
(6)设x,y满足
(A)有最小值2,最大值3 (B)有最小值2,无最大值
(C)有最大值3,无最小值 (D)既无最小值,也无最大值
(7)等比数列 的前n项和为 ,且4 ,2 , 成等差数列。若 =1,则 =
(A)7 (B)8 (3)15 (4)16
(8) 如图,正方体 的棱线长为1,线段 上有两个动点E,F,且 ,则下列结论中错误的是
(A)
(B)
(C)三棱锥 的体积为定值
(D)异面直线 所成的角为定值
(9)已知O,N,P在 所在平面内,且 ,且 ,则点O,N,P依次是 的
(A)重心 外心 垂心 (B)重心 外心 内心
(C)外心 重心 垂心 (D)外心 重心 内心
(注:三角形的三条高线交于一点,此点为三角型的垂心)
(10)如果执行右边的程序框图,输入 ,那么输出的各个数的合等于
(A)3 (B) 3.5 (C) 4 (D)4.5
(11)一个棱锥的三视图如图,则该棱锥的全面积(单位:c )为
(A)48+12 (B)48+24 (C)36+12 (D)36+24
(12)用min{a,b,c}表示a,b,c三个数中的最小值
设f(x)=min{ , x+2,10-x} (x 0),则f(x)的最大值为
(A)4 (B)5 (C)6 (D)7
第II卷
二、填空题;本大题共4小题,每小题5分。
(13)设已知抛物线C的顶点在坐标原点,焦点为F(1,0),直线l与抛物线C相交于A,B两点。若AB的中点为(2,2),则直线 的方程为_____________.
(14)已知函数y=sin( x+ )( >0, - < )的图像如图所示,则 =________________
(15)7名志愿者中安排6人在周六、周日两天参加社区公益活动。若每天安排3人,则不同的安排方案共有________________种(用数字作答)。
(16)等差数列{ }前n项和为 。已知 + - =0, =38,则m=_______
三、解答题:解答应写出说明文字,证明过程或演算步骤。
(17)(本小题满分12分)
为了测量两山顶M,N间的距离,飞机沿水平方向在A,B两点进行测量,A,B,M,N在同一个铅垂平面内(如示意图),飞机能够测量的数据有俯角和A,B间的距离,请设计一个方案,包括:①指出需要测量的数据(用字母表示,并在图中标出);②用文字和公式写出计算M,N间的距离的步骤。
(18)(本小题满分12分)
某工厂有工人1000名, 其中250名工人参加过短期培训(称为A类工人),另外750名工人参加过长期培训(称为B类工人),现用分层抽样方法(按A类、B类分二层)从该工厂的工人中共抽查100名工人,调查他们的生产能力(此处生产能力指一天加工的零件数)。
(I)求甲、乙两工人都被抽到的概率,其中甲为A类工人,乙为B类工人;w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(II)从A类工人中的抽查结果和从B类工人中的抽插结果分别如下表1和表2.
表1:
生产能力分组
人数 4 8
5 3
表2:
生产能力分组
人数 6 y 36 18
(i)先确定x,y,再在答题纸上完成下列频率分布直方图。就生产能力而言,A类工人中个体间的差异程度与B类工人中个体间的差异程度哪个更小?(不用计算,可通过观察直方图直接回答结论)w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(ii)分别估计A类工人和B类工人生产能力的平均数,并估计该工厂工人的生产能力的平均数,同一组中的数据用该组区间的中点值作代表)w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(19)(本小题满分12分)
如图,四棱锥S-ABCD 的底面是正方形,每条侧棱的长都是地面边长的 倍,P为侧棱SD上的点。
(Ⅰ)求证:AC⊥SD;w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(Ⅱ)若SD⊥平面PAC,求二面角P-AC-D的大小
(Ⅲ)在(Ⅱ)的条件下,侧棱SC上是否存在一点E,w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
使得BE‖平面PAC。若存在,求SE:EC的值;
若不存在,试说明理由。
(20)(本小题满分12分)
已知椭圆C的中心为直角坐标系xOy的原点,焦点在s轴上,它的一个顶点到两个焦点的距离分别是7和1.
(Ⅰ)求椭圆C的方程;
(Ⅱ)若P为椭圆C上的动点,M为过P且垂直于x轴的直线上的点, =λ,求点M的轨迹方程,并说明轨迹是什么曲线。w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(21)(本小题满分12分)
已知函数
(I) 如 ,求 的单调区间;
(II) 若 在 单调增加,在 单调减少,证明
<6. w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
请考生在第(22)、(23)、(24)三题中任选一题作答,如果多做,则按所做的第一题记分。作答时用2B铅笔在答题卡上把所选题目对应的题号涂黑。
(22)本小题满分10分)选修4-1:几何证明选讲w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
如图,已知 的两条角平分线 和 相交于H, ,F在 上,
且 。
(I) 证明:B,D,H,E四点共圆:
(II) 证明: 平分 。w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(23)(本小题满分10分)选修4—4:坐标系与参数方程。
已知曲线C : (t为参数), C : ( 为参数)。
(1)化C ,C 的方程为普通方程,并说明它们分别表示什么曲线;
(2)若C 上的点P对应的参数为 ,Q为C 上的动点,求 中点 到直线
(t为参数)距离的最小值。w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(24)(本小题满分10分)选修4-5:不等式选讲
如图,O为数轴的原点,A,B,M为数轴上三点,C为线段OM上的动点,设x表示C与原点的距离,y 表示C到A距离4倍与C道B距离的6倍的和.
(1)将y表示成x的函数;
(2)要使y的值不超过70,x 应该在什么范围内取值?w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
2009年普通高校招生全国统一考试
理数数学试题参考答案
一. 选择题
(1) A (2) D (3) C (4) A (5) A (6) B
(7) C (8) D (9) C (10) B (11) A (12) C
二.填空题
(13) (14) (15) 140 (16) 10
三.解答题
(17) 解:
方案一:①需要测量的数据有:A
点到M,N点的俯角 ;B点到M,
N的俯角 ;A,B的距离 d (如图)
所示) . ……….3分
②第一步:计算AM . 由正弦定理 ;
第二步:计算AN . 由正弦定理 ;
第三步:计算MN. 由余弦定理 .
方案二:①需要测量的数据有:
A点到M,N点的俯角 , ;B点到M,N点的府角 , ;A,B的距离 d (如图所示).
②第一步:计算BM . 由正弦定理 ;
第二步:计算BN . 由正弦定理 ;w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
第三步:计算MN . 由余弦定理
(18) 解:
(Ⅰ)甲、乙被抽到的概率均为 ,且事件“甲工人被抽到”与事件“乙工人被抽到”相互独立,故甲、乙两工人都被抽到的概率为w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
.
(Ⅱ)(i)由题意知A类工人中应抽查25名,B类工人中应抽查75名.
故 ,得 ,
,得 .
频率分布直方图如下
从直方图可以判断:B类工人中个体间的关异程度更小 .
(ii) ,
,
A类工人生产能力的平均数,B类工人生产能力的平均数以及全工厂工人生产能力的平均数的会计值分别为123,133.8和131.1 .
w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(19)解法一:
(Ⅰ)连BD,设AC交BD于O,由题意 。在正方形ABCD中, ,所以 ,得 .
(Ⅱ)设正方形边长 ,则 。
又 ,所以 ,
连 ,由(Ⅰ)知 ,所以 , w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
且 ,所以 是二面角 的平面角。
由 ,知 ,所以 ,
即二面角 的大小为 。
(Ⅲ)在棱SC上存在一点E,使
由(Ⅱ)可得 ,故可在 上取一点 ,使 ,过 作 的平行线与 的交点即为 。连BN。在 中知 ,又由于 ,故平面 ,得 ,由于 ,故 .
解法二:
(Ⅰ);连 ,设 交于 于 ,由题意知 .以O为坐标原点, 分别为 轴、 轴、 轴正方向,建立坐标系 如图。
设底面边长为 ,则高 。
于是
w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
故
从而
(Ⅱ)由题设知,平面 的一个法向量 ,平面 的一个法向量 ,设所求二面角为 ,则 ,所求二面角的大小为
(Ⅲ)在棱 上存在一点 使 .
由(Ⅱ)知 是平面 的一个法向量,
且
设 w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
则
而
即当 时,
而 不在平面 内,故
(20)解:
(Ⅰ)设椭圆长半轴长及半焦距分别为 ,由已知得
,w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
所以椭圆 的标准方程为
(Ⅱ)设 ,其中 。由已知 及点 在椭圆 上可得
。
整理得 ,其中 。
(i) 时。化简得 w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
所以点 的轨迹方程为 ,轨迹是两条平行于 轴的线段。
(ii) 时,方程变形为 ,其中
当 时,点 的轨迹为中心在原点、实轴在 轴上的双曲线满足 的部分。
当 时,点 的轨迹为中心在原点、长轴在 轴上的椭圆满足 的部分;
当 时,点 的轨迹为中心在原点、长轴在 轴上的椭圆;
(21)解:
(Ⅰ)当 时, ,故
w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
当
当
从而 单调减少.
(Ⅱ)
由条件得: 从而
因为 所以
将右边展开,与左边比较系数得, 故
又 由此可得
于是 w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(22)解:
(Ⅰ)在△ABC中,因为∠B=60°,
所以∠BAC+∠BCA=120°.
因为AD,CE是角平分线,
所以∠HAC+∠HCA=60°,
故∠AHC=120°.
于是∠EHD=∠AHC=120°.
因为∠EBD+∠EHD=180°,
所以B,D,H,E四点共圆.
(Ⅱ)连结BH,则BH为∠ABC的平分线,得∠HBD=30°
由(Ⅰ)知B,D,H,E四点共圆,
所以∠CED=∠HBD=30°.
又∠AHE=∠EBD=60°,由已知可得EF⊥AD,
可得∠CEF=30°.
所以CE平分∠DEF. w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
(23)解:
(Ⅰ)
为圆心是( ,半径是1的圆.
为中心是坐标原点,焦点在x轴上,长半轴长是8,短半轴长是3的椭圆.
(Ⅱ)当 时,
为直线
从而当 时,
(24)解:
(Ⅰ)
(Ⅱ)依题意,x满足
{
解不等式组,其解集为9,23
所以
w.w.w.k.s.5.u.c.o.m
2008海南省高考英语作文题目是什么?
2012年高考英语模拟试卷(含答案)(试卷总分:120分 考试时间:100分钟)
第Ⅰ卷(选择题 共85分)
第一部分:英语知识运用(共两节,满分45分)
第一节 单项填空(共15小题;每小题1分,满分15分)
从A、B、C、D 四个选项中,选出可以填入空白处的最佳选项。
1. —The garden has four gates in different directions, so you may enter it and relax through any of them in the daytime.
—_______.
A. Very good B. Very convenient C. That’s good D. I like it
2. —I ran into _______ back of _______ truck yesterday and damaged my car badly.
—I suppose you were driving too fast.
A. the; the B. a; a C. the; a D. a; the
3. Visitors can stand on the top of Oriental Pearl Television Tower, from where they can have a better ______ of the city of Shanghai.
A. sight B. scenery C. scene D. view
4. Medicine should not be kept _______ it is accessible to children.
A. which B. where C. how D. that
5. The village which they lived in for many years _______ by Typhoon Morakot and now there is nothing to be seen.
A. was destroyed B. has been destroyed C. destroyed D. had destroyed
6. Many of them turned a deaf ear to his advice, even though they knew it to be _______.
A. valuable B. reliable C. flexible D. acceptable
7. Hillary Clinton arrived in Pyongyang on August 4, 2009, ______ the start of the short visit to Korea.
A. marked B. having marked C. marking D. to mark
8. The color of the shirt does not _______ that of the tie.
A. fit B. match C. suit D. reach
9. But for your help, we _______ the game.
A. can lose B. will lose
C. had lost D. would have lost
10. She was very fond of speaking French, _______ indeed she spoke well.
A. which B. that C. of which D. how
11. _______, they make mistakes as part of their everyday behavior.
A. Not only humans make mistakes B. Not only do humans make mistakes
C. Only humans make mistakes D. Only do humans make mistakes
12. One cause of this attitude students have can be represented by the fact _____ young teachers don’t know how to impose their respect among their students.
A. which B. that C. why D. /
13. I don't want to _______ the topic, but why on earth did you get home that late last night?
A. take up B. make up C. break up D. bring up
14. 一Did you tell him that we’ve put off the meeting?
一No. He rushed out before I could say ________.
A. something B. nothing C. anything D. everything
15. I won't have anyone _______ in here. Whoever breaks the regulation will get punished.
A. to smoke B. smoke C. smoked D. smoking
第二节 完形填空(共20小题,每题1.5分,共30分)
阅读下面短文,撑握其大意,然后从16—35各题所给的四个选项(A、B、C和D)中,选出最佳选项。
Before discussing different kinds of emotions, let us briefly talk about how researchers 16 bodily processes, actions and behavior, and how this relates to what we do in our daily lives when we observe emotions in 17 .
Bodily processes can be directly measured by 18 of a polygraph. When a polygraph is skillfully used to 19 how we react bodily with what we are 20 , it is called a "lie detector". Bodily processes can also be measured 21 . This is what we do when we observe someone blushing (脸红). However, we are not always 22 of what bodily processes respond to.
Measuring action 23 behavior is the other way researchers assess the emotions. 24 , one measure of fear of snakes is how 25 a person will go to the snake. Another procedure is to have a person 26 how afraid he is, or how he feels, in this way, researchers have 27 the so-called "fear thermometer" to assess a person's fear. 28 our everyday living, we do very much the same thing. Only not too 29 . We react to what a person does, what he says, 30 he says it, and how he looks. Is he smiling? Is his voice trembling? We put all this 31 together to infer what a person is feeling.
32 , we do not always act as we feel. Sometimes we do things that we don't feel like doing. 33 we say we feel one way and then we act another. Actors, for example, successfully learn to "make believe" emotions, or learn to 34 them. Thus we 35 always tell what a person is feeling by what he says or by what he does.
16. A. measure B. describe C. make D. use
17. A. other B. others C. another D. the others
18. A. ways B. methods C. means D. tools
19. A. combine B. treat C. examine D. compare
20. A. doing B. saying C. observing D. carrying
21. A. directly B. indirectly C. easily D. difficultly
22. A. afraid B. fond C. aware D. accused
23. A. but B. so C. and D. or
24. A. For example B. On one hand C. As well as D. At times
25. A. slow B. fast C. far D. close
26. A. tell B. say C. talk D. speak
27. A. approved B. discovered C. developed D. informed
28. A. During B. With C. On D. In
29. A. skillfully B. systematically C. naturally D. eventually
30. A. why B. where C. how D. whether
31. A. imaginations B. observations C. impressions D. awareness
32. A. Therefore B. Otherwise C. However D. Anyway
33. A. Sometime B. Someway C. Sometimes D. Anytime
34. A. express B. hide C. act D. say
35. A. needn’t B. shan’t C. won’t D. cannot
第二部分 阅读理解(共20小题;每小题2分,满分40分)
阅读下列短文,从每题所给的四个选项(A、B、C和D)中,选出最佳选项。
A
Stephen William Hawking was born on 8 January 1942 (300 years after the death of Galileo) in Oxford, England. His parents' house was in north London, but during the Second World War Oxford was considered a safer place to have babies. When he was eight, his family moved to St Albans, a town about 20 miles north of London. At eleven Stephen went to St Albans School, and then on to University College, Oxford, his father's old college. Stephen wanted to do mathematics, although his father would have preferred medicine. Mathematics was not available at University College, so he did Physics instead. After three years and not very much work he was awarded a first class honours degree in Natural Science.
Stephen then went on to Cambridge to do research in Cosmology, there being no-one working in that area in Oxford at that time. His supervisor was Denis Sciama, although he had hoped to get Fred Hoyle who was working in Cambridge. After gaining his Ph.D. he became first a Research Fellow, and later on a Professorial Fellow at Gonville and Caius College. After leaving the Institute of Astronomy in 1973 Stephen came to the Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, and since 1979 has held the post of Lucasian Professor of Mathematics. The chair was founded in 1663 with money left in the will of the Reverend Henry Lucas, who had been the Member of Parliament for the University. It was first held by Isaac Barrow, and then in 1663 by Isaac Newton.
Professor Hawking has twelve honorary degrees, was awarded the CBE in 1982, and was made a Companion of Honour in 1989. He is the recipient of many awards, medals and prizes and is a Fellow of The Royal Society and a Member of the US National Academy of Sciences.
36. Stephen W. Hawking went to the same college as _________at his teenage.
A. Galileo B. his father C. Isaac Barrow D. Isaac Newton
37. Which of the following shows the right order of what happened to Hawking?
a. He gained his Ph.D.
b. He went to Cambridge.
c. He was given a first class honor degree.
d. He began to hold the post of Lucasian Professor of Mathematics. ecbad
e. He went to St Albans School.
A. e-c-b-a-d B. a-e-c-d-b C. a-e-c-b-d D. c-b-d-e-a
38. According to the passage, Stephen W. Hawking had never spent much time studying _______.
A. Cosmology B. Mathematics C. Physics D. Medicine
39. Before Stephen Hawking went to Cambridge, ____________.
A. there was no one studying cosmology in England.
B. There was no one studying cosmology in Oxford
C. There were only a few scientists studying cosmology in Oxford
D. Cosmology is widely studied in Britain.
其余的见参考资料。(文件太大,传不上。)
假定你是李华,从小喜爱大熊猫,一直通过有关网站关注三年前在美国圣迭哥动物园出生的大熊猫"苏琳"和她的母亲"白云"。现在苏琳即将三岁。请根据以下要点给动物园工作人员写一封信:
1.自我介绍;
2.祝贺苏琳生日;
3.感谢工作人员;
4.索取苏琳三岁生日照。
注意;1.词数100左右; 2.可以适当增加细节,以使行文连贯; 3.开头语已为你写好。
范文:
Dear Sir/Madam,
Greetings from China!
I’m Li Hua, a student in Sichuan. I’ve been a panda lover since I was a child. About three years ago I was delighted to learn that Baiyun gave birth to her daughter Sulin and I’ve been watching her grow on your website. Now she’s going to be three .I’d like to wish her a happy birthday and to express my thanks to you for your hard work, because of which Sulin and her parents are living a happy and healthy life in the US.
By the way, could I have a photo of Sulin taken on her third birthday? Thank you very much in advance.
Yours truly,
Li Hua